What Is an IBAN Number and How Does It Work?
- Published: 24 July 2024
- 13 min read
- Running a Business


Heather Cameron
Author
Heather is here to inform and inspire our readers. Boasting eight years in the world of digital marketing, working in diverse industries like finance and travel, she has experience writing for various audiences. As Osome’s resident copywriter, Heather crafts compelling content, including expert guides, helpful accounting tips, and insights into the latest fintech trends that will help entrepreneurs, founders and small business owners in Hong Kong take their businesses to the next level.

Sherman Ieong
Reviewer
Sherman Ieong is our Accounting & Tax Manager based in Hong Kong. She is on hand to help our writers level-up our blog posts and guides by making sure the information is accurate, informative and inspiring. Osome’s all-in-one accounting services make managing tax effortless - and that’s exactly what Sherman ensures we do with our Hong Kong-focused blog content, applying her knowledge of day-to-day bookkeeping, monthly financial reporting, Profits Tax Returns and much more.
An IBAN number (International Bank Account Number) is crucial for international banking transactions. It ensures that payments across borders are accurate and efficient. This guide will explain an IBAN number, how it works, and why you need it, including its role in identifying the bank code and facilitating SEPA credit transfers.
Key Takeaways
- The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is a standardised alphanumeric code used to identify overseas bank accounts and facilitate efficient and accurate global transactions, including the precise identification of the bank code and branch code.
- IBANs consist of up to 34 alphanumeric characters, including a country code, check digits, and a Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN), which varies by country and includes the bank identifier code and branch code. This ensures precise identification of bank accounts.
- IBAN numbers, critical for international payments, help reduce errors, enhance the speed of transactions, and are securely validated by banks using specialised algorithms to ensure accuracy and prevent fraudulent activities. This process ensures that each international transaction is correctly processed.
What Is an IBAN Number?
The International Bank Account Number, or IBAN, is an international numbering system used to identify international bank account numbers. This universal identifier ensures financial institutions worldwide can process international transactions more efficiently and accurately, as it includes the necessary bank code for each account. International bank account numbers (IBANs) are important for sending and receiving international banking payments across countries and jurisdictions, providing a standardised format for precise identification.
The IBAN number system was born out of the efforts of European banks to simplify and automate transactions involving international transactions. In 1997, the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) published ISO 13616:1997, the basis of today's IBAN, facilitating efficient international organisation for standardisation. This standardisation was a big step towards a single way of identifying international bank accounts, reducing errors through the use of international bank account numbers.
It’s like an international address for your individual bank account. With all this information in one IBAN number, international banks can pinpoint the exact account to which you’ll send money. This reduces the risk of errors and delays with just account numbers. IBANs are common in Europe and many other regions but are becoming more global, providing a standardised format for identifying international bank account numbers and bank codes.
Navigating international financial regulations and ensuring accurate IBAN information can be complex. Osome can help! We offer a comprehensive suite of services, including company registration. Let us handle the complexities so you can focus on global growth. Contact us today!
Structure of an IBAN
The meticulously designed structure of an IBAN offers a comprehensive and standardised format for identifying international bank accounts, including the bank code. An IBAN number consists of up to 34 alphanumeric characters, each serving a specific purpose in the identification process. The first component of an IBAN is a two-letter country code, which immediately identifies the country where the account is held. This is followed by two check digits, which play a crucial role in validating the integrity of the entire IBAN number.
The Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN), which includes the bank code, follows the country code and check digits, ensuring accurate identification of your IBAN number. This portion of the IBAN number contains specific bank and account details, including the bank identifier code, and its structure can vary from country to country. The BBAN, serving as a form of bank account identification, is determined by the banking association of each country, allowing for some flexibility within the standardised IBAN framework. The BBAN's inclusion of the branch code further ensures precise identification.
A combination of standardised elements and country-specific details render the IBAN number a potent tool for identifying individual bank accounts across disparate nations and financial systems. Additionally, the system is internationally recognised for its effectiveness in global financial operations.
Example of an IBAN Format
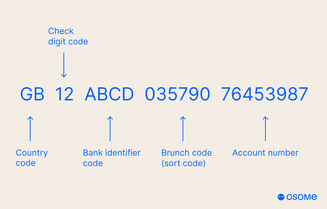
To better understand the structure of an IBAN, let’s consider a hypothetical IBAN example from Hong Kong: HK12 1234 5698 7654 3210. In this IBAN, the structure is as follows:
- “HK” represents the two letter country code for Hong Kong
- The two check digits are “12”
- The remaining characters constitute the Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN), which includes the bank identifier code and the specific bank account number.
One should note that the format of IBAN can vary significantly between countries. For instance, while Norway uses a 15-character IBAN, Liechtenstein employs a 21-character format. This variation in length and structure underscores the flexibility of the IBAN system in accommodating different national banking standards while maintaining a standardised international format. Each IBAN example demonstrates how file organisation techniques are applied differently across countries.
How Do IBAN Numbers Work?
The working principle of IBAN numbers is simple: they act as the linchpin of international banking transactions, ensuring cross-border payments get to the right bank account. When an international transfer is made, the IBAN plays a key part in identifying the sender and recipient accounts for an international transaction. This starts with the beneficiary giving their IBAN to the ordering customer, who then uses this information to set up the transfer. Additionally, the ordering customer may need the SWIFT code of the recipient’s bank. This combination ensures the funds are accurately directed to the specific financial institution.
Before the transfer is processed, the ordering customer’s bank does a key check on the IBAN to ensure a secure international transaction. This check is to catch any errors early and prevent misdirected payments and the hassle that comes with them. The bank’s payment system runs the IBAN characters through its database, utilising specialised algorithms to verify the account details contained within the IBAN. This thorough check ensures that the IBAN corresponds to a valid account and that all the details are correct before initiating the transfer. Additionally, the central bank might also verify the associated SWIFT code to ensure all the information matches the intended recipient’s financial institution.
The algorithms used in the IBAN verification system do the following:
- Digest and check the account info in the IBAN
- Add an extra layer of security and accuracy
- Flag potential issues like typos or invalid account details
By doing this, banks can verify IBANs and ensure the accuracy of SWIFT codes used in conjunction with IBANs.

This verification process:
- Reduces failed transfers and rejected payments
- Simplifies the international payment process
- Speeds up international transactions by ensuring accurate SWIFT codes and account details are used
Why IBAN Numbers Were Created?
The purpose of creating the IBAN numbers was to solve the problem of international banking, especially within the Eurozone. After the euro was introduced in 1999, there was a big push for a single payment area to make cross-border transactions easier. This initiative gained significant momentum with the Payment Services Directive (PSD) 2007, which laid the groundwork for creating the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA), finalised in 2014. The European Committee played a crucial role in this development.
IBAN numbers were designed to help with payments between Eurozone banks to address several international banking challenges within the European Union countries. The main goals were:
- Reduce cross-border payment errors
- Improve verification using SWIFT codes and other identifiers
- Minimise rejected payments, transfer delays and associated bank charges and fees.
By providing a standardised format for account identification across different countries, IBAN numbers have significantly streamlined the process of international money transfers, making them faster, more accurate, and more cost-effective.
This standardisation has been key to international trade and transactions in a more globalised world, supported by the International Organization for Standardization and other international organisations.
Differences Between IBAN, SWIFT, and BIC Codes
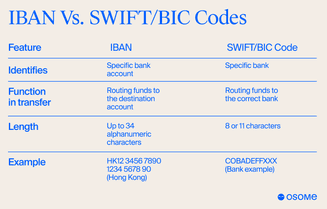
IBAN, SWIFT and BIC are all important for international banking, but each serves a different purpose and contains different information. The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) identifies individual bank accounts for domestic and international transactions, especially within the SEPA area. It includes the bank account number, country code, and a full account identifier. SEPA credit transfers are facilitated using IBANs to ensure efficient and accurate processing. These identifiers are recognised and standardised by the International Organization for Standardization.
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) codes, BIC (Bank Identifier Codes) or swift codes do something different. They are used to identify the bank during international transactions. A SWIFT or BIC code is 8-11 characters long and includes a bank, country, and location code. Unlike IBANs, which identify individual accounts, SWIFT and BIC codes identify the institution that holds the account. These business identifier codes are crucial for ensuring that funds are directed to the correct financial institution.
The difference lies in their use: IBAN identifies account details, country, and individual account number, while SWIFT and BIC codes identify the country, bank, and branch of the recipient’s account. The SWIFT system enables bank communication by transmitting payment instructions and data to process international transactions correctly. The combination of IBAN for account identification and SWIFT/BIC for bank identification is a solid system for cross-border payments, ensuring accurate and efficient handling of funds by the designated payment authority.
In short, IBAN and SWIFT (or BIC) codes are both important for international money transfers, but they tell different parts of the story—IBAN is where (specific account) and SWIFT/BIC is to whom (specific bank).
Where To Find Your IBAN Number?
Finding your IBAN number is usually straightforward, with various options available based on your bank’s services and banking preferences. The most convenient way for many individual account holders is to check their online banking platform. Most banks provide IBAN number information within their online banking interfaces, often listed under account information or in a dedicated section related to international payments. If you’re comfortable with digital banking, this should be your first port of call.
For those who prefer traditional banking methods or need a physical record, checking their bank statement is another reliable option for identifying bank accounts. IBAN numbers are usually prominently displayed at the top of bank statement documents. For easy reference, you might even find your IBAN number printed directly on your bank card in some countries.
If you cannot locate your IBAN number through these methods, don’t hesitate to contact your bank directly. By providing them with your individual account details, they can supply you with your IBAN number. Additionally, some (but not all) banks offer online IBAN calculators where you can input your country code, sort code, and account number to generate your international bank account number.
How To Use IBAN Numbers for International Transfers?
Using IBAN numbers for international transfers represents a critical facet of contemporary global banking. When initiating a cross-border payment, the IBAN serves as the primary identifier for the recipient’s account. This standardised format ensures that the payment is directed to the correct account, minimising errors and delays. To complete an international transfer, you’ll typically need both the IBAN and the SWIFT code of the recipient’s bank. While the IBAN identifies the specific account, the SWIFT code pinpoints the exact bank and branch.
Within the Eurozone, transfers have been further streamlined through the SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) system. A SEPA Credit Transfer utilises IBAN numbers to process payments efficiently, often completing transactions within one working day. This system has significantly reduced the time and complexity of transferring money between European countries, making it almost as simple as domestic transfers.

For even faster transactions, overseas banks identify SEPA Instant Credit Transfers as a solution. SEPA Credit Transfer services allow for near-instantaneous transfers between SEPA Instant Credit-registered accounts. When both the sender and recipient’s accounts are registered for this service, transfers can be completed in as little as 10 seconds after confirmation. This rapid processing time represents a significant advancement in international banking, offering unprecedented speed and convenience for transfers within the SEPA zone.
Security of IBAN Numbers
IBAN number security is a top priority in the global banking system, and IBANs are considered safe for international transactions. Eurozone regulators have approved using IBANs for fund transfers as they help with secure and fast international payments. Sharing your IBAN doesn’t pose a direct risk to your funds as it only allows someone to send money to your account, not to withdraw from it.
IBAN numbers serve as a safeguarding system, incorporating a verification process that checks account data before funds are transferred between international banks. This built-in verification helps to reduce errors and prevent fraudulent activities. Additionally, the standardised format of IBAN numbers aids in quickly identifying and flagging potential issues, further enhancing the security of international transactions.
Despite the innate security features of IBAN numbers, account holders must exercise caution and adhere to best practices to safeguard their financial information. Banks typically advise customers to:
- Don’t share your IBAN with anyone; only share with trusted parties to prevent fraud.
- Using someone else’s IBAN without permission is fraud and can be illegal.
- Banks have measures to detect unauthorised access using someone else’s IBAN, an additional layer of protection for you.
Countries That Use IBAN Numbers
The IBAN system has seen widespread adoption, with numerous countries incorporating this standardised format into their international banking practices, supported by the European Committee. According to the latest IBAN Registry, 86 countries have embraced the IBAN system, although some sources report the current number as 77. This global adoption includes other European countries, countries in the Middle East, and the Caribbean, demonstrating the system’s versatility and effectiveness across different regions and financial environments.
While the IBAN system has gained considerable traction, it’s important to note that several major economies have not adopted it for domestic use. Notable exceptions include:
- United States
- Canada
- Australia
- New Zealand
- China

However, these countries still recognise and process IBAN-based payments for international transactions. For instance, in the United States, IBAN numbers are used exclusively to send money to foreign bank accounts participating in the IBAN system. This hybrid approach allows seamless integration with IBAN-using countries while maintaining their local banking standards for domestic transactions.
Common Issues with IBAN Numbers
Despite the benefits of IBANs in international banking, users can still encounter certain issues with IBANs when making transactions due to differences in bank account numbers. The most common problem is incorrect IBAN entry, which can result in the following:
- rejected or delayed payments
- inconvenience
- extra fees charged by the banks involved
- funds sent to the wrong recipient can lead to a complex and time-consuming recovery process.
Remember, having the correct IBAN format is important, but it doesn’t mean the IBAN exists or belongs to the intended account. That’s why it’s crucial to verify IBANs before making transactions. Many banks and financial institutions have IBAN number checkers which can validate the format and structure of an IBAN. However, these tools can’t confirm if the IBAN is actually associated with the intended recipient’s account. So always double-check the IBAN with the recipient or their bank before transferring, especially for large or important transactions.
Benefits of Using IBAN Numbers
There are numerous advantages to using IBAN numbers. They are the superheroes of international money transfers. IBAN numbers streamline the process, saving you time and frustration and ensuring your money lands safely in the intended account.
One of the biggest advantages of IBANs is their accuracy. Traditional account numbers can be tricky, with variations in format and length depending on the bank. IBANs eliminate this confusion by providing a standardised format that incorporates details about your bank, branch, and account number, all wrapped up with a handy country code. This precision minimises the risk of typos or errors that could delay or even derail your transfer.
IBANs also speed up the entire process. Because they contain all the necessary routing information, the banks involved can efficiently identify the recipient's account, meaning your money gets there faster.

Security is another area where IBANs shine. The built-in error-checking mechanisms in IBANs help prevent fraudulent transactions. Since the code carries so much information, any inconsistencies are flagged during the transfer process, making it more difficult for unauthorised parties to divert your funds.
Also, IBAN promotes better information exchange between countries and financial institutions. The standardised format makes tracking and reconciling payments across borders easier and simplifies accounting for international businesses. This uniformity also enables more complex and integrated international banking systems to develop and bring about future innovations in global finance. As the world gets more connected, the role of IBAN in international payments will only get more critical.
So, the next time you need to send money internationally, ask for the recipient's IBAN. It's the key to a smoother, faster, and more secure transfer experience.
Thinking of taking your business international? Osome can help! We offer a comprehensive suite of services, including company registration. Let us guide you through the process and ensure a smooth global expansion. Contact us today!
Summary
In conclusion, the International Bank Account Number (IBAN) system has revolutionised the landscape of international banking, offering a standardised, efficient, and secure method for identifying bank accounts across borders. From its structure and functionality to its widespread adoption and security features, IBAN numbers facilitate seamless global financial transactions. While challenges such as input errors persist, the benefits of using IBANs – including reduced errors, faster processing times, and improved information exchange – far outweigh these issues. As the global economy integrates, understanding and effectively utilising IBAN numbers becomes increasingly important for individuals and businesses. By embracing this system and following best practices, we can contribute to a more connected and efficient international financial ecosystem, opening doors to new opportunities in the global marketplace.






