Company Financial Statements: A Beginner's Guide
- Modified: 20 March 2025
- 13 min read
- Bookkeeping, Tax & GST


Heather Cameron
Author
From expert guidance and helpful accounting tips to insights on the latest trends in fintech, Heather is here to empower entrepreneurs and small business owners in Singapore with great content. With a background in digital marketing spanning eight years, she has experience writing for various industries and audiences. As Osome’s copywriter, she’s here to inform and inspire our readers with great storytelling.

Kelly Yik
Reviewer
Kelly Yik, our Accounting Team Lead based in Singapore, ensures that the team meets quality standards and follows accounting standards (SFRS) while remaining compliant with all the authorities' rules and regulations in Singapore. With six years of experience in Singapore accounting, she knows the ins and outs of financial reporting standards, GST, and corporate tax like nobody's business. Kelly supports our blog writers by carefully reviewing our content, making sure it's accurate, up-to-date, and packed with helpful tips for Singapore businesses. So, you can trust the info you get on our blog is not only interesting but also reliable!
A financial statement provides a clear picture of a business’s financial health. It includes documents like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement and companies rely on these statements to make informed decisions. This guide will explain the components and functionalities of these three statements.
Key Takeaways
- Financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, are essential tools for evaluating a company’s financial health, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions.
- The balance sheet demonstrates a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity; the income statement tracks profitability over time; and the cash flow statement highlights liquidity and cash management.
- Despite their importance, financial statements have limitations, such as potential interpretive biases and lack of non-financial information, but leveraging technology like AI and automation can improve their accuracy and efficiency.
What Are Company Financial Statements?
A company financial statement tracks how a business is performing financially. Different statements can help stakeholders understand a company's financial health at a specific time, showing what a company owns (assets), owes (liabilities), as well as its equity, cash flows, and total income. This determines bookkeeping as one of the key elements of the company.
Investors, creditors, and even the company's own managers rely on these reports to understand how the business is doing. They're like a financial compass, guiding decisions about investments, loans, and future strategies. By comparing reports from different periods, stakeholders can see trends, evaluate how well management is doing, and make smart choices that keep the company moving forward.
Understanding these financial statements can be complex, but you don't have to go it alone. Osome offers comprehensive bookkeeping services. We'll help you decipher your financial statements, identify areas for growth, and make informed decisions that propel your business forward. Contact us today!
What Are the Types of Financial Statements?
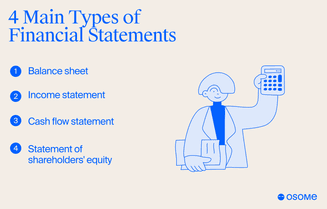
Four core financial statement s form the foundation of financial reporting: balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of shareholders' equity. Each report gives different insights into the company’s financial performance and position.
- The balance sheet is a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and each shareholder's equity at a specific time.
- The income statement measures profitability over some time by showing revenues, expenses, and net income.
- The cash flow statement records cash inflows and outflows, showing the company’s liquidity and financial management.
- The statement of shareholders' equity shows how much profit the company has retained (kept) or paid out as dividends to shareholders.
These reports are prepared regularly, monthly for internal reporting and quarterly or annually for external disclosure. These three financial statements give you a complete picture of the company’s financial position so you can dive deeply into annual reports and make informed decisions based on audited reports.
Balance Sheet
A company's balance sheet displays what the company owns (total assets), what it owes (total liabilities), and how much money belongs to the owners (shareholder equity) at a specific time. This also includes no cash expenses and cash equivalents. Additionally, the balance sheet shows if the company is spending more than it earns or has a healthy cushion of assets.
The equity section on a balance sheet lays out common stock and the stock price, which tells investors how much their shares in the company's stock are worth.
The snapshot of the financial position
This financial snapshot is super important! It tells investors and other interested folks whether the company is financially sound and a good investment. Imagine it as a quick check-up – is the company loaded with cash and equipment (assets) or drowning in debt (liabilities)?
The balance sheet reflects a business's financial well being at a specific point in time. So, next time you hear about a balance sheet, remember it's not just some accounting term – it's a powerful tool for understanding a company's financial well-being!
Assets and liabilities
The balance sheet breaks down assets and liabilities into current and non-current by liquidity and payback period. Current assets (cash and accounts receivable) can be converted to cash within a year. Non-current assets (property and equipment) can’t. Current liabilities (accounts payable) are debts or obligations due within a year. Non-current liabilities (mortgages and bonds) are due after a year. Finally, unrealised gains are recorded in the comprehensive income section.
Understanding these categories helps stakeholders determine whether the company can pay short-term debts and manage long-term commitments. For example, high current liabilities might mean liquidity issues, and big non-current assets might mean a big investment in the company’s future growth.
Shareholders' equity
A company is like a pie. Shareholders’ equity is the slice left over after you take out all the bills the company owes (liabilities). This slice is made up of a few things: the money shareholders initially invested (common stock), any extra cash they put in on top (additional paid-in capital) and the profits the company decided to keep and reinvest in itself (retained earnings). Think of retained earnings like returning your birthday money to your piggy bank to buy something even cooler later.
Investors can get an idea of the company's health by looking at how the company uses this shareholder pie. They use fancy terms like “return on equity” (ROE) to see how much profit the company makes from each dollar shareholders invest. Another tool, the “debt-to-equity” (D/E) ratio, compares the pie slice to the total debts to see how much they owe versus what they own. This helps investors see if the company is too dependent on borrowing.
Income Statement
Also known as the profit and loss statement, the income statement shows a company’s profitability over a period of time by listing revenues, expenses, and net income. This piece in the financial statement gives a complete view of the financial results of the company’s operations and is important for measuring the company’s performance.
Tracking profitability
The income statement is an important tool for tracking a company’s profitability. It lists all revenues and expenses for a period and ends with the net income. By reading this, you can see how the company is managing its costs and making profits over time.
Key items on the income statement are operating income (EBIT) which includes earnings before interest and tax; non-operating income, such as interest payments, and net income, which is the final figure after all expenses and taxes are deducted. For example, Amazon’s income statement combines the cost of sales with other expenses like fulfilment and marketing to calculate operating income, which gives a clear view of its core performance.
Revenue and expenses
Revenue and expenses on the income statement are divided into operating and non-operating items. Operating revenue is from the company’s main business activities, such as sales of products or services. This is usually at the top of the income statement and includes gross values before deducting the costs of getting those sales.
The main expenses are the cost of goods sold (COGS), the direct cost of producing goods or services and selling, and general and administrative (SG&A), the overhead cost. By comparing these revenue and operating expenses, you can see the company’s core business and financials, including gross profit.
Net income and earnings per share
Net income is:
- Total revenue minus total expenses, including taxes.
- The company’s gross profit is key to understanding its financial performance.
- It also flows into retained earnings on the balance sheet, the cumulative profit reinvested in the business.
Earnings per share (EPS) is another important metric calculated by dividing net income by the number of shares outstanding. EPS is the earnings per share of stock, giving investors a profit per share measure.
Cash Flow Statement
Each line item in the cash flow statements records a company’s cash flows so you can see how well the company manages its cash to pay debts, fund operations and invest in growth. It is one of the most important accounting basics to level up finances and grow your business.
Understanding cash movement
Cash flow statements demonstrate where you’re spending too much or not bringing in enough. For example, it might show you’re holding onto too much stock so you can adjust your ordering habits.
The line items also explain how the company funds itself. Is it borrowing or issuing new stock to raise cash? Are they paying back debt or giving money back to shareholders through dividends? This financial picture helps investors see how the company manages its money and stays afloat.
These financing activities are like backstage jobs: issuing stock is like bringing in new investors, taking out a loan is like getting a credit card, and paying dividends is like sharing profits with the audience. By looking at these activities, you can see how healthy the company’s finances are and if they are a good investment.
Operating activities
Cash flow from operating activities reflects cash generated from the company’s core business operations. Analysts note it as the most important measure of performance. A decrease in cash flow from operations can signal trouble selling products or collecting money from customers, highlighting potential issues in the company’s operational efficiency.
This section includes non-cash items, changes in working capital and other items that affect operating cash. By looking at these numbers, you can see how well the company generates cash from its main activities.
Investing and financing activities
Investing activities cover cash flows related to long and short term investments. Common investing activities include purchasing or selling long term assets such as properties, buildings, and equipment. Cash flow from investing also includes loans to vendors or customers, payments for mergers or acquisitions, and purchases of fixed assets.
Financing activities include cash flows related to raising or repaying capital. This includes:
- borrowings
- shares issued
- share buybacks
- dividends paid
Now you know how the company is funding itself.
Statement of Shareholders' Equity
The statement of shareholders’ equity logs changes in equity over time, mirroring the company’s financial activities and ownership interests. This statement reports changes in equity accounts, including:
- comprehensive income
- changes in accounting policies
- corrections of errors
- additional money invested by owners
- dividends distributed to shareholders.
Retained earnings are a significant component of shareholders’ equity. These earnings reflect the total profits generated by the business, excluding dividends or distributions to shareholders. This reinvestment helps fuel future growth and expansion, illustrating the company’s commitment to long-term success.
How Financial Statements Are Connected?
Financial statements are linked together to give a complete picture of a company’s financial position. This linked financial statement approach means net income is recorded at the bottom of the income statement and shows up on both the cash flow statement and the statement of retained earnings. This is why net income is so important to understanding a company’s performance.
An accountant can explain how net income affects retained earnings in the shareholder’s equity section of the balance sheet, which is the starting point for cash flows from operations on the cash flow statement. Changes in current assets and liabilities on the balance sheet are adjusted on the cash flow statement so you can see how all the statements are connected.
Why Financial Statements Are Important for Business Growth?
Financial statements are crucial for business growth. They track everything – how much money comes in, how much goes out, and where it all goes. This lets companies see what's working well and where they can improve. Strong financials, like good grades on a report card, can boost a company's reputation and stock price, making it easier to attract investors and grow.
Financial statements help investors to judge a company's health and identify problems early on. For example, a profitability ratio shows how good a company is at turning a profit from its core business. With this financial wisdom, businesses can prioritise spending, cut waste, and keep growing on the path to success.

Common Accounting Principles and Standards
Reporting requirements may vary between different companies. For example, a private company and a public company follow different reporting rules. That's where common accounting standards come in handy.
Singapore companies should refer to IFRS as a universal guideline. It is a global standard used almost everywhere except the US. It's more like a set of principles than strict rules.
It is also important to understand your local accounting rules. For example, audited financial statements are required for private limited companies in Singapore. The Companies Act mandates that private limited companies in Singapore audit their annual financial statements for reporting purposes.
Challenges and Limitations of Financial Statements
Despite their importance, financial statements come with challenges and limitations:
- They can be interpreted differently, such as in terms of debt levels and information reliability.
- Financial statements are influenced by management’s judgement and estimates, which can be biased.
- They don’t always reflect the current gross asset value and comprehensive income.
Moreover, financial statements don’t capture non-financial information. Financial statement analysis is useful but can be misinterpreted if not compared correctly or if its context is ignored. Therefore, companies sometimes rely on audited financial statements for enhanced accuracy.
Leveraging Technology for Financial Reporting
Automation and AI can increase reporting efficiency, accuracy and data analysis. Some core benefits behind automation are:
- Quick and accurate complex financial tasks, less manual work and errors
- Data accuracy and control over financial data
- Less human error
AI and machine learning can help with forecasting and decision-making by analysing large data sets. Cloud solutions offer scalability and offsite storage for financial data, blockchain provides an immutable log of transactions, and financial records are more reliable. Digital dashboards allow decision-makers to see key performance indicators without sacrificing accuracy or compliance.
While automation is powerful, navigating the complexities of financial reporting, including understanding and interpreting these reports, requires human expertise. Osome offers comprehensive accounting services beyond just bookkeeping or secretarial services. We'll provide expert guidance to ensure your financial statements are clear and insightful and drive strategic growth for your business. Contact us today!
Summary
Understanding and effectively utilising a company financial statement is essential for making informed business decisions and driving growth. The balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement provide comprehensive health and performance insights. By mastering these documents, stakeholders can evaluate business performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions that foster long-term success. Governed by common accounting rules and standards, financial statements also ensure reporting consistency and comparability.
Finally, technology can enhance the reporting processes with different financial institutions, improving efficiency and accuracy. By integrating these tools, businesses can gain real-time insights and maintain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market. Embrace the power of financial statements, and let them guide your journey towards business excellence.






