A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting and Forecasting
- Published: 18 March 2024
- 13 min read
- Grow Your Business


Gabi Bellairs-Lombard
Author
Gabi's passionate about creating content that inspires. Her work history lies in writing compelling website copy and content, and now specialises in product marketing copy. When writing content, Gabi's priority is ensuring that the words impact the readers. As the voice of Osome's products and features, Gabi makes complex business finance and accounting topics easy to understand for small business owners.
Why juggle numbers without direction? Master the art of budgeting and forecasting – your business’s financial compass. In this guide, we’ll direct you through crafting a financial plan that not only reflects your strategic vision but also prepares you for the future events, ensuring your business doesn’t just survive but thrives.
Key Takeaways
- Budgeting is a financial plan that establishes goals and tracks progress, while forecasting uses historical data to predict future financial performance and inform strategic adjustments.
- Both budgeting and forecasting are instrumental in financial management, offering benefits like guiding resource allocation, identifying risks and opportunities, and aligning financial strategies with business goals.
- Leveraging technology in budgeting and forecasting improves efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making with automation, reducing errors and promoting collaboration through integrated software for responsive financial planning.
What Is Budgeting and Forecasting?
Budgeting and forecasting are financial management practices businesses use to plan and manage their finances effectively. They serve as a roadmap, guiding businesses towards their strategic direction. But how exactly do they work, and why are they so crucial? Let’s dive in to find out.
Budgeting is the cornerstone of a company’s financial plan. It involves setting financial goals for a specific period, aligning financial resources and activities with these goals, and tracking progress towards achieving them. It typically includes estimates of revenue and expenses, as well as expected revenues, cash flow and debt reduction. It helps businesses set practical financial targets, allocate resources effectively, and track actual results against set targets. These detailed plans serve as a robust framework for informed financial management.
On the other hand, forecasting uses historical data and assumptions to predict future results. It provides an overall picture of financial performance, minimises uncertainty by anticipating future trends, and facilitates stability by comparing forecasted results with actual outcomes. This approach allows businesses to:
- Adjust their budgets and spending in response to actual business performance
- Identify potential risks and opportunities
- Make informed decisions about resource allocation
- Set realistic goals and targets
- Communicate financial expectations to stakeholders
Our dedicated and experienced accountants can help you create comprehensive budgeting and forecasting for your business.
By using forecasting techniques, businesses can better plan for the future and make strategic decisions to drive growth and success.
Both the budgeting and forecasting process are critical roles in a company’s financial health and achieving revenue growth. Translating a company’s strategic plan into actionable financial resources and targets allows businesses to stay resilient against risks and consistently achieve their financial goals.
The role of budgeting
Budget plays a frontline role in the grand scheme of a business's planning process and working towards impactful revenue growth. The roadmap aligns financial resources and activities with the company’s strategic goals and objectives. It provides a clear direction for achieving long-term success. Determining pathways to meet objectives such as increased profits integrates these targets into the budget as measurable and achievable goals. With the budget acting as a guiding light, a management team can effectively allocate resources, ensuring they are investing in the business's financial success.
By tracking actual results against set financial targets, businesses can conduct variance analysis and make informed decisions for performance improvement.
Benefits of budgeting
Budgeting is not just about crunching numbers for a fiscal year – it’s about understanding your company’s financial activities and making strategic decisions. It forces management to:
- Examine the company’s financial activities
- Assess the viability of each expense
- Document all the sources and uses of cash
- Accurately anticipate cash flows
The budgeting process offers several benefits, including:
- Instilling a sense of ownership among employees, motivating them to meet their budgeted goals
- Providing real-time insight into how your company is performing through periodic comparison of the budget against up-to-date financial results
- Clarifying individual responsibilities and promoting rapid responses to challenging situations
- Ensuring that financial reserves are allocated appropriately to keep the business on track
The role of forecasting
If budgeting is the roadmap, forecasting is the compass that guides a business towards its financial goals. It uses a company’s historical financial data and assumptions to predict future results, providing an overall picture of financial performance. Accurate forecasting minimises uncertainty and risk by anticipating future trends and changes in key performance indicators, which is essential for making informed strategic decisions.
Forecasting ensures financial stability by allowing businesses to adjust their budgets and spending in response to actual performance. Forecasting contributes to accurate predictions of future financial outcomes, whether applied to short-term, medium-term, or long-term periods. Because forecasts change regularly due to market conditions or business plan adjustments, executives must monitor performance regularly and act accordingly.
Benefits of forecasting
Just like a weather forecast helps you plan your outfit for the day, financial forecasting helps you plan your business strategies. It reveals business trends that can help determine if you need to adjust its course. It becomes easier to manage cash flows, income statements, balance sheets and capital requirements with well-informed predictions of where future expenses are likely to fluctuate. Reliable forecasts can help you capitalise on financing and investment opportunities.
Most importantly, forecasting complements budget planning process by providing a logical starting point for your next budget. It allows managers to focus their attention where it’s needed, especially in the short term.
Essential Components of Budgeting
A comprehensive business plan, complete with an annual budget, is a versatile tool that can aid businesses in achieving success. To effectively budget for the upcoming fiscal year, management teams must analyse past financial statements to understand revenue trends and allocate resources appropriately.
It involves:
- Setting goals and priorities
- Gathering financial information
- Allocating resources
- Estimating expenses and revenue
- Incorporating elements like cash flows and capital expenditures for a specific period
A successful budgeting process includes:
- Navigating spending patterns
- Categorising expenses
- Identifying opportunities for optimisation
- Ensuring the accommodation of both short-term obligations and long-term financial goals to maintain financial stability.
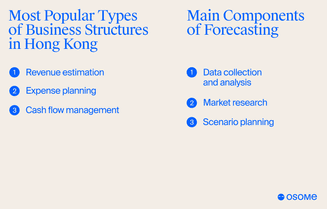
Revenue estimation
An essential component of a budget planning process is revenue estimation at the start of a calendar or fiscal year. It involves listing core products and services, along with their pricing, to project expected revenue volumes for the upcoming year. This estimation process necessitates a detailed consideration of products or services being sold, their prices, and the estimated volumes.
To validate the reliability of these estimates, it’s critical to understand the key drivers and assumptions influencing expenses and sales projections.
Expense planning
While revenue estimation fuels the engine of your budget, expense planning ensures that you don’t run out of gas. It includes regular payments such as:
- rent or mortgage
- employee salaries
- insurance
- loan interest
- utilities
These expenses usually remain unchanged over the budget period and fiscal year. Alongside fixed costs, it also includes variable costs that can change monthly. Distinguishing between essential and non-essential expenses is crucial, allowing for prioritising spending and identifying areas where cost savings can be achieved.
Forecasting additional spending, such as one-off expenses not regularly occurring in the budget, is also a critical component of expense planning. Simple budgeting and forecasting software can be used to streamline this process — Osome's app is an easy-to-use tool that many business owners use to get a quick insight into their business's cash cycle, providing them with efficient decision-making.
Cash flow management
Cash flow management is the steering wheel of your budget, guiding your business towards financial stability. It involves:
- Strategic forecasting
- Efficient management of receivables and payables
- Cost control
- Regular analysis to optimise cash flow and working capital
Regular scrutiny of cash movement is vital in the planning process, ensuring alignment between money coming in and out with the budgeted amounts.
Proactively managing inventory and vendor relationships can also help optimise working capital management. To improve cash flow, businesses should reduce liabilities and enhance assets through debt reduction. Strategies such as selling unused assets and stimulating sales to gain short-term clients can be beneficial.
Essential Components of Forecasting
Forecasting guides businesses through uncertain financial waters like a ship’s compass. It is based on historical trends and uses data to estimate future business outcomes, playing a crucial role in planning and anticipating financial outcomes.
Data collection and analysis
The foundation of any reliable forecast is data. Forecasting relies heavily on historical data and trends to predict future business outcomes, guiding production, resource allocation, and strategic decisions.
There are various methods including
- liquidity analysis
- profitability analysis
- leverage analysis
- solvency analysis
- cash flow analysis
- trend analysis
- turnover ratio analysis
- efficiency analysis
to identify financial trends and risks.
Maintaining a database of key revenue and expense metrics and regularly evaluating economic activity can improve data accuracy for forecasting. Some steps to consider include:
- Centralising financial, sales, and operational data
- Regularly evaluating economic activity
- Improving data accuracy for forecasting
- Enabling better alignment and cooperation across different company teams
These steps are crucial in scenario planning.
Market research
Market research is the wind in the sails of financial forecasting. It is critical for:
- Understanding target markets
- Marketing products and services effectively
- Comprehending consumer behaviour
- Anticipating market shifts
Accurate market research can reduce risks and pinpoint optimal investment timing. Insights from top performers inform growth-oriented decisions.
Interviews, surveys, industry reports, and case studies are among the key primary and secondary methods employed in financial market research. The use of AI and machine learning in online surveys reduces errors and improves data quality for financial market research.
Scenario planning
Scenario planning is the rudder of your financial forecast, steering your business towards a secure future. It evaluates uncertainties, risks, and opportunities of potential future scenarios, accounting for potential risks and enabling organisations to prepare for disruptions. Scenario planning aids in:
- Testing different actions to see their influence on outcomes
- Considering future customer preferences
- Analysing competitor moves
- Adapting to overall market changes
By incorporating scenario planning into your business strategy, you can better navigate future uncertainties and make informed decisions.
Forecasting with scenario planning helps companies:
- Develop risk mitigation strategies
- Ensure resilience against economic downturns or market fluctuations
- Make necessary adjustments in response to unforeseen events
What Are the Methods of Budget Forecasting?
Budget forecasting methods are the navigational tools that chart the course of your financial journey. They include historical data analysis, which examines past financial data to determine trends and patterns that can be used to predict future performance. Regression analysis identifies the relationship between sales and other factors, such as marketing spend or economic indicators.
Time series analysis determines seasonal patterns and trends to forecast future performance. Scenario analysis helps identify potential risks and opportunities and develop contingency plans. Expert opinion involves soliciting input from individuals with specialised knowledge/experience in a particular area.
Budget-to-actual analysis helps identify areas where the budget may need to be revised or adjusted based on actual performance. Lastly, rolling forecasts adapt to changing market conditions and identify potential risks and opportunities in real-time.
What Is the Difference Between Budgeting and Forecasting?
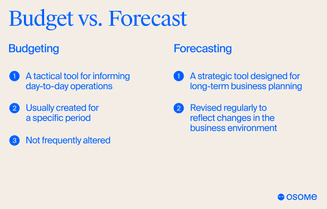
Budgeting and forecasting are two sides of the same coin, each with its unique characteristics. Budgets are plans for spending based on estimates of expenses and income over a period, while forecasts predict what will actually be achieved. Budgets are more detailed and are used to determine financial needs and resources, whereas forecasts are more strategic and high-level.
Budgeting is a tactical tool for informing day-to-day operations, and forecasting is a strategic tool designed for long-term business planning. Budgets are usually created for a specific period, such as a fiscal year or monthly, and are not frequently altered, while forecasts are revised regularly to reflect changes in the business environment.
Integrating Budgeting and Forecasting
Like a well-oiled machine, budgeting and forecasting work best when they’re integrated. They’re critical for making smart decisions and handling budgets effectively.
Forecasting often precedes budgeting, as it helps predict future performance, estimate revenue and expenses, and subsequently allocate resources, ensuring targets are based on informed insights.
Aligning goals and projections
Aligning business goals with financial forecasts is critical for effective resource allocation, ensuring financial capabilities support strategic plans. Key Performance Indicators, such as operating cash flow and sales figures, are crucial in setting realistic budgets and revenue estimations.
Promoting collaboration among different departments leads to more comprehensive insights, which can dramatically enhance the accuracy of budget forecasts. Scalable budgeting solutions, which provide clearer visibility into financial data, enable organisations to make more informed decisions and quickly adapt to financial changes.
Monitoring and adjusting
Monitoring and adjusting budgets is like fine-tuning a musical instrument – it ensures your financial performance remains in perfect pitch. Continually monitoring and adjusting the budget is vital to remain aligned with evolving financial circumstances and manage finances proactively. Budgets must be dynamic, with regular reviews essential to guide the organisation towards its goals.
Establishing regular milestones in budgets and forecasts helps gauge if the business stays on the planned trajectory and aligns with management objectives. Financial forecasts must be frequently updated to allow organisations to remain responsive to market changes and support continuous improvement.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Budgeting and Forecasting
As with any journey, budgeting and forecasting come with their own set of challenges. However, these challenges can be overcome, such as timeframes, variables requiring course corrections, and complexities determined by a company’s size, structure, or industry. By adhering to key principles, effective budgeting and forecasting are achievable for organisations of all sizes.
Inaccurate data
One of the main pitfalls in this exercise is inaccurate data. It can be caused by factors such as:
- Data entry errors
- Non-standardised data collection
- Delayed posting
- Outdated accounting systems
- Untracked procurement data
Inaccurate data negatively impacts business decision-making, potentially leading to poor choices that could hurt the company financially.
Regular auditing and validation of financial data is key to maintaining accuracy and reliability, and enhancing the forecasting and budgeting process.
Lack of collaboration
Lack of collaboration can be a barrier in this important business exercise. Cross-functional collaboration is integral for synchronising budget and forecast planning within an organisation. The involvement and engagement of peers and stakeholders are critical for forecasts' accuracy and obtaining organisational commitment.
Improved budget planning and resource allocation are outcomes of effective communication and stakeholder collaboration in forecasting exercises.
Resistance to change
Resistance to change can be a significant hurdle in adopting a new budgeting and forecasting process. Communicating a clear and compelling vision of the new processes can help overcome resistance by highlighting the benefits and creating a sense of urgency. Involvement of stakeholders and encouraging their input and expertise can help identify cost-saving opportunities and increase their sense of ownership and commitment to new processes.
Training and education for stakeholders can enhance their understanding of and openness to adopting new budgeting processes or tools.
Leveraging Technology for Budgeting and Forecasting
Technology is the wind beneath the wings of budgeting and forecasting. Integrated budget management solutions enhance transparency across organisational levels and facilitate improved stakeholder collaboration.
Organisations are replacing spreadsheets with real-time data and integrated systems for more agile financial management. Manual processes are no longer suitable for growth or ever-changing market conditions.
Automation and efficiency
In the world of budgeting and forecasting, automation and efficiency go hand in hand. Some benefits of using advanced financial software include:
- Reducing errors in forecasting and budgeting
- Automated data entry, which saves time and reduces errors
- Allowing greater focus on analysis and forward planning
Automation tools reduce the time spent on data entry and calculations, boosting overall productivity.
Real-time data access
Real-time data access is like having a bird’s eye view of your financial landscape. It allows for more accurate and informed decision-making as business opportunities arise. Continuous close practices in accounting, supported by modern software, aim to provide 24/7 access to accurate financial data.
Real-time access to financial data improves cash flow by enabling faster billing cycles through automated workflows based on project milestones.
Scalability and flexibility
Budgeting and forecasting tools that scale and flex with your business are like a well-fitted suit – they enhance performance and comfort. Scalable budgeting and forecasting software can improve financial planning and analysis, providing better transparency into financial drivers and enabling quicker responses for sensitivity analysis with the help of forecasting software.
Flexibility in budgeting tools allows for the required level of detail, avoiding the burden of overly detailed forecasts that may require frequent adjustments.
Summary
In conclusion, budgeting and forecasting are vital tools in financial planning. They provide a roadmap and compass for businesses, guiding them towards their financial goals. Businesses can improve their financial planning and decision-making by understanding their roles, benefits, methods, and challenges.
FAQ
What is forecasting and budgeting in food production?
Forecasting in food production involves estimating future trends and outcomes based on past and present data, while budgeting is preparing a financial plan for the forthcoming period. Both skills are essential for effective planning and strategy adjustments in food and beverage organisations.
What are the 5 steps of the budgeting process?
To create a budget, first calculate your net income, list your monthly expenses, label fixed and variable expenses, determine average monthly costs for each expense, and make adjustments to fit your financial goals.
What are the key differences between budgeting and cash forecasting?
Budgeting involves planning income and spending, while cash forecasting predicts the timing of cash flow into and out of a bank account. Both are important for financial management, but they serve different purposes.
What is the role of budgeting in financial planning?
Budgeting is crucial in financial management as it helps in setting financial targets, allocating resources, and monitoring progress towards those goals, ultimately serving as a roadmap for strategic direction.
What are the common budgeting and forecasting challenges?
Budgeting and forecasting commonly face challenges like timeframes, variables requiring course corrections, and complexities determined by a company's size, structure, or industry. These factors can make the process more difficult to navigate.
Get expert tips and business insights
By clicking, you agree to our Terms & Conditions,Privacy and Data Protection Policy
We’re using cookies! What does it mean?






